Damiana Exposed: Special Look At Turnera diffusa (2023)
Damiana is a wild shrub native to Central and South America that has long been celebrated for its myriad uses and benefits. Known scientifically as Turnera diffusa, it boasts yellow flowers and aromatic leaves, which have found their place in both traditional and modern medicinal practices.
In the following sections, we’ll journey back to explore its origins and historical significance. We’ll then switch our lens to examine the plant from a botanical perspective, detailing its physical attributes and natural habitat.
The subsequent sections will uncover its traditional and contemporary uses, shedding light on its psychoactive characteristics and how these can be harnessed.
Finally, we’ll guide you through the different ways to use it, discuss recommended dosages, and caution against known side effects.
Whether you’re a botanical veteran, a health-conscious individual, or simply someone intrigued by the world of medicinal plants, you’ll want to keep reading to learn more about kanna.
History of Damiana
Damiana is a fascinating plant with a deep-rooted history that spans continents and cultures. This section will explore the origins, historical significance, and cultural beliefs associated with this unique herb.

Origins
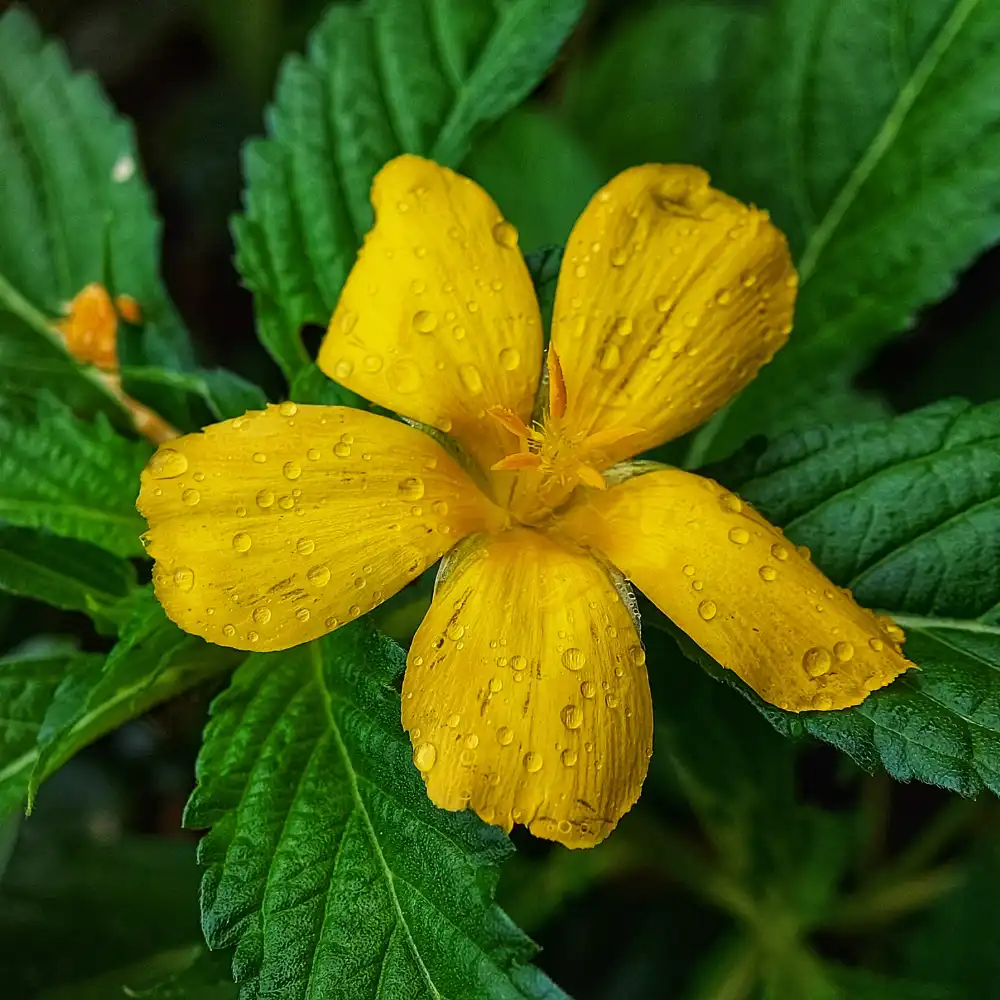
Damiana, scientifically known as Turnera diffusa, or Turnera aphrodisiaca , traces its roots to various regions including southern Texas in the U.S., Central America, Mexico, South America, and the Caribbean.
It is part of the Passifloraceae family, which is notable for its diverse species of flowering plants. Growing as a small, woody shrub, it showcases its beauty in early to late summer when it blooms with small, aromatic flowers.
The flowering phase is followed by the production of fruits that bear a resemblance in taste to figs, adding to the plant’s unique charm. One of the distinguishing features of the plant is its strong, spice-like odor, which is often compared to chamomile.
Historical Significance
Damiana has a rich and fascinating history. It was initially used by indigenous cultures of Mexico and Central America, including the Mayans and Aztecs, for its medicinal properties.
These ancient civilizations revered it as a powerful plant with aphrodisiac properties, using it to enhance sexual desire and performance. Moreover, its calming effects were well recognized, and it was often used to treat anxiety, nervousness, and mild cases of depression.
It was also used as a general tonic to improve wellness and health. In the 19th century, it began to gain popularity in Western societies.
It was introduced into the U.S. Pharmacopoeia in 1888 as a treatment for various conditions including menstrual problems, constipation, and respiratory issues. Today, its historical significance continues to resonate as research delves deeper into understanding its potential benefits and uses.
Its traditional role as a natural aphrodisiac and mood enhancer is still valued in many cultures around the world. This enduring legacy underscores its importance in the fields of botany and herbal medicine.
Cultural Beliefs and Traditions
The plant’s influence extends beyond its medicinal uses, permeating various cultural beliefs and traditions. These cultural practices, deeply rooted in history, further illustrate its significance.
Among certain indigenous tribes of Mexico, it was considered sacred. It was often used in religious ceremonies and rituals, believed to facilitate communication with spirits and deities.
This spiritual connection was attributed to its psychoactive properties, which could induce a relaxed and slightly euphoric state. In addition, it held a prominent place in traditional Mexican liqueur recipes.

The leaves were steeped in alcohol to create a unique beverage that was not only enjoyed for its taste but also its supposed aphrodisiac effects. This tradition has persisted over the centuries, and today, damiana-infused liqueurs continue to be a popular choice in certain regions of Mexico.
Furthermore, in some South American cultures, it was used as a symbol of fertility and love. It was often included in wedding ceremonies, intended to bless the newlyweds with prosperity and a harmonious marital life.
These cultural beliefs and traditions underscore its multifaceted role throughout history. From its therapeutic uses to its spiritual significance and social relevance, its impact is truly diverse and far-reaching.
Ethnobotany
Before getting into what it’s for and how to benefit from it, here are some basic facts about the plant itself.
Scientific Classification
As presented at a University of Mississippi conference in 2009, this perennial herb is a member of the large Passifloraceae family, which encapsulates around 750 species spread across 27 genera. In terms of its order, damiana belongs to the Malpighiales, which is one of the largest orders of flowering plants.
The genus of this plant, Turnera, comprises approximately 120 species, with Turnera diffusa, or damiana, being one of the most recognized due to its medicinal properties. This scientific classification underscores the plant’s diversity and its unique characteristics within the botanical world.
Physical Attributes
Damiana is a small shrub that grows between 2 -6 feet in height and is easily recognizable by its slender stems covered in smooth, serrated leaves. The leaves are aromatic and when crushed, they exude a strong, distinctive scent similar to chamomile.
They are usually about 4-10 inches long, and their color can range from a bright green to a more subtle gray-green. The flowers are small, about a half inch in diameter, and bloom in early to late summer.
They are also yellow (usually), five-petaled, and have a sweet, fig-like fragrance. After they bloom, the plant produces small fruits that resemble tiny figs.
The fruit has a sweet and spicy flavor, which led to its use in the traditional Mexican liqueurs discussed above. The root system of the plant is extensive and robust, allowing it to thrive in the arid conditions of its natural habitat.
The roots are typically harvested along with the leaves for their medicinal properties. Overall, the physical attributes of damiana contribute not only to its survival in harsh environments but also to its appeal as a medicinal and therapeutic herb.

Natural Habitat and Geographical Distribution
This is a plant that thrives in subtropical climates. Its natural habitat stretches from southern Texas in the United States, across Central America, and down to South America. It is also found in the Caribbean islands.
This plant is highly adaptable and can endure a variety of environmental conditions. Its geographical distribution indicates it prefers dry, sandy, and rocky places. The robust root system allows the plant to survive in these arid conditions.
Despite its extensive distribution, its growth rate and lifespan can vary depending on environmental factors or location. This adaptability contributes to its widespread presence and its ability to thrive in diverse habitats.
Growth and Harvest
Damiana is a hardy plant that exhibits a strong growth cycle, flourishing best under full sun exposure with optimal soil drainage conditions. It’s considered a drought-tolerant plant and can thrive even in poor soil conditions, making it well-suited for the natural, arid environments it’s typically found in.
The plant generally blooms in the late spring to early summer, with its yellow flowers transforming into fruits over time. When it comes to harvesting, the leaves are the primary focus as they contain the valuable compounds and essential oils that make this plant so sought after.
The best time to harvest the leaves is typically in the summer, just after the plant has flowered. This is when the leaves are considered to be at their most potent, infused with the maximum level of beneficial constituents.
The harvesting process involves carefully picking the leaves from the plant, ensuring to not damage the stems or the roots. Once harvested, they need to be dried properly before they can be utilized.
This is typically done by spreading them out in a thin layer in a shaded, well-ventilated space, away from direct sunlight. Once completely dried, these can be stored in an airtight container for future use.
Damiana in Traditional Medicine
In the realm of traditional medicine, damiana has been used for centuries, particularly among indigenous tribes in Central and South America. The Mayans, for instance, utilized damiana as an aphrodisiac, believing in its ability to boost sexual potency and desire.
It was also used to treat a variety of ailments, including digestive issues, respiratory problems, and anxiety. The leaves of damiana, often prepared as a tea or tincture, were hailed for their stimulant properties.

Native healers used damiana leaf infusions to combat fatigue and enhance physical endurance. The plant was also used as a mood enhancer, aiding in the relief of mild depression, anxiety, and mood swings.
In Mexican folk medicine, it was prescribed as a general tonic to improve overall well-being. It was used to balance hormonal function, stimulate the digestive system, and support the body’s natural detoxification processes.
The leaves were also smoked as a mild relaxant, delivering a calming, euphoric effect. Moreover, damiana was used in traditional medicine for its diuretic and antiseptic properties.
It has been used to treat urinary tract infections and bladder issues, thanks to its antimicrobial constituents.
While these traditional uses of damiana underscore its widespread medicinal applications, it’s crucial to note that many of these benefits are based on anecdotal evidence and traditional knowledge.
Unfortunately, natural remedies do not get much credible published research as many tend to compete with mainstream pharmaceuticals, which are extremely profitable for the corporations who own their patents.
Phytochemistry & Current Potential Medicinal Applications
On a pharmacological level, damiana is believed to exert its effects by interacting with various neurotransmitter systems in the human body and mind. It does this through its wide array of plant compounds.
Research indicates that the plant matter itself is composed of several active phytochemicals. These include essential or volatile oils that contain elements like cineol, cymol, and pinene. It also has flavonoid antioxidants, which are universally recognized for their health benefits.
Another component found in damiana is caffeine, a well-known stimulant. Additionally, compounds such as pinocembrin, acacetin, gonzalitosin, and damianin are present.
The herb also contains arbutin and tannin, along with thymol, a natural monoterpenoid phenol derivative of cymene.
Sexual Health
Research has shown that damiana has potential benefits when it comes to sexual health and overall vitality. It is often used as a natural remedy to improve sexual health in both men and women. Some studies suggest that it may relieve sexual dysfunction caused by antidepressants.
A 1999 journal article titled “Aphrodisiac properties of Turnera diffusa,” ostensibly validates its long-standing reputation as a natural aphrodisiac. Conducted on sexually exhausted male rats, the research found that the administration of damiana significantly improved sexual behavior patterns.
The plant exhibited a positive impact on parameters such as potency, number of intromissions, and ejaculations. Consequently, the study concluded that damiana may have potential applications in the treatment of certain types of sexual dysfunction.

These findings were replicated in another animal study in 2009 when its components were found to have a positive impact on sexual performance equal to that of Yohimbe.
More empirical data published in PLoS ONE evaluated the testicular protection conferred by damiana against amitriptyline-induced testicular toxicity and DNA damage. The results showed that it offers a significant protective effect on sex hormone levels.
However, it’s important to note that while some studies have reported positive outcomes, others have suggested potential risks. For example, prolonged administration of damiana resulted in increased toxic effects on the kidney in matured Wistar rats, similar to the effects of alcohol.
Anxiety
Aside from its role in sexual health, damiana is also recognized for its potential mood-enhancing properties. It is often used in herbal remedies designed to alleviate symptoms of anxiety, depression, and mood swings.
Multiple studies suggest that one of its chemical compounds, apigenin, may have anxiolytic effects, making it a natural alternative for managing stress and promoting relaxation.
It is known to bind to benzodiazepine receptors in the brain, which play a crucial role in reducing anxiety, inducing sleep, and creating a relaxation effect. A study published in the Journal of Natural Products highlighted apigenin’s potential neuroprotective effects.
The study showed that apigenin can exhibit potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, and it may be beneficial in neurodegenerative diseases.
Further, a 2005 study published in Pharmaceutical Biology found these effects to be significant at doses of 2 mg/kg orally in mice, which equates to about 13 mg for humans based on industry-standard calculations.
Another documented the plant’s anxiolytic properties and potential as a treatment for anxiety. The study administered damiana at human equivalent doses of 40, 56, and 85 mg, observing the behavior of male Wistar rats using a common method to assess anxiety in rodents
It was noted that it significantly decreased anxiety-like behavior, which serves as even stronger evidence supporting its traditional use as a calming agent.
Digestion
Additionally, damiana continues to be used for digestive health. Its leaves are often brewed into a tea which is believed to improve digestion and alleviate constipation. Its potential to stimulate the gastrointestinal tract can also aid in detoxification, favoring overall health and wellness.
Aromatase Inhibition
Recent studies have pointed to damiana’s potential role as an aromatase inhibitor. According to a study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology, damiana was found to inhibit the activity of the enzyme aromatase, which plays a crucial role in the biosynthesis of estrogens.
Aromatase inhibition is a key strategy in the management of estrogen-dependent diseases like certain types of breast cancer.
Research has shown that a methanolic extract from damiana leaf can inhibit the activity of the aromatase enzyme in laboratory settings, with an IC50 value (the concentration required to inhibit 50% of the enzyme’s activity) being 63.1mcg/mL.
When isolated compounds from the leaf were tested, both pinocembrin and acacetin were found to be effective. At a concentration of 10μM, pinocembrin inhibited 50.5% and acacetin inhibited 42.6% of aromatase activity.
The IC50 values for pinocembrin and acacetin were found to be 10.8μM and 18.7μM respectively. This research opens up promising avenues for damiana’s potential use in mitigating conditions that require the regulation of estrogen levels.
These findings were backed up by the results of additional research performed eight years later by the Department of Pharmacy at the University of Naples Federico II in Italy, when apigenin was again found to inhibit the aromatase enzyme.
Fat Loss
In the realm of dietary supplements, damiana extracts are now included as a key ingredient in many weight loss products. It’s believed to aid in weight loss by inducing thermogenesis – a metabolic process in which your body burns calories to produce heat.
A research study published in the Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics investigated the effects of a South American herbal preparation containing yerbe maté, guarana, and damiana on gastric emptying and weight loss.
The study found that the herbal mixture delayed gastric emptying and promoted weight loss when used over a 45-day period in a controlled primary healthcare setting.
Results from another study done by a group of researchers at a Mexican university examined the effects of damiana on diabetic rats, ultimately concluding that it promoted body weight loss in these animals.
Furthermore, as mentioned above, it has been found to have anti-aromatase activity, meaning it may help to reduce the conversion of testosterone to estrogen, which can contribute to weight gain.

Blood Sugar
A study in 2017 investigated the anti-diabetic effects of one of the plant’s key components, teuhetenone. The researchers found that in normoglycemic mice, this compound exhibited hypoglycemic activity.
It was observed to gradually reduce glucose levels over a period of six hours. The study also evaluated teuhetenone A’s effects in a murine model of diabetes. The results showed a reduction in glucose levels of approximately 35%, further demonstrating its antidiabetic activity.
The effects were found to be comparable to those of insulin, which is a standard diabetes treatment. The group found no inhibition of α-glucosidase, an enzyme involved in carbohydrate digestion, which shows the mechanism of action to be unique when compared to other treatments.
Antioxidant Activity
If you are not familiar with them beyond their general name, antioxidants are compounds that can prevent or slow damage to cells caused by free radicals, unstable molecules that the body produces as a reaction to environmental and other pressures.
A study published in the Journal of Natural Products Research found that a water-ethanol/damiana extract had significant antioxidant effects. Since oxidative stress goes hand-in-hand with the progression of diabetes, the findings potentially make the case for a new alternative treatment for the disease.
Another research article investigated the antiphotoaging effects of damiana leaf extract by evaluating the expression of certain antioxidant regulators.
The results confirmed that the leaves possess antioxidant effects, which could potentially protect against photoaging, a process that can lead to premature skin aging due to exposure to sunlight and ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
Pain Relief
A study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology explored the analgesic properties of damiana, particularly focusing on one of its components, apigenin. The results revealed that apigenin possesses potent analgesic effects.
In the study, apigenin was administered to mice, resulting in a significant decrease in abdominal writhing, a common response to discomfort or pain in animals.
Additionally, apigenin demonstrated properties consistent with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and possessed anti-nociceptive effects in both thermal and chemical pain models.
This indicates the potential of damiana, specifically its component apigenin, to act as a natural pain reliever. Since it would take an enormous amount of plant material to reach the apigenin levels used in this study, an extract version would be much more practical.
Anti-cancer Activity
One key area of interest is damiana’s rich content of apigenin, a flavonoid that has shown significant anti-cancer effects in various studies, which are best summed up in this meta-analysis. This compound has consistently shown the potential to inhibit the growth of various types of cancer cells, including breast, colon, skin, thyroid, and leukemia cells.
The studies suggest that it achieves this result through various mechanisms such as inducing apoptosis (programmed cell death), inhibiting cell proliferation, and impeding angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels that feed tumors).
Psychoactive Attributes of Damiana
Damiana’s psychoactive properties are predominantly attributed to its longtime use as an aphrodisiac and a mood enhancer. These qualities are largely due to compounds called terpenes found in its leaves, which have a direct impact on our nervous system.
Mood Enhancement
Many users report a subtle mood elevation after consumption, describing it as a feel-good sensation or a mild euphoria. Research indicates that the plant’s impact on mood may be linked to its interaction with dopamine, a neurotransmitter vital for mood regulation, attention, and reward.
Its constituents are thought to interact with the dopaminergic system, potentially influencing dopamine’s affinity to D2 receptors, thereby affecting mood enhancement. Furthermore, they might inhibit dopamine absorption, which could contribute to an increase in available dopamine
Aphrodisiac Effect
The most renowned psychoactive effect of damiana is its aphrodisiac properties. Traditionally, it has been used to increase sexual desire and performance, primarily due to its ability to increase blood flow and oxygenation levels in the sexual organs.
Study data suggests that it may also influence hormonal systems, potentially enhancing sexual receptivity and performance.
Relaxation and Mild Sedation
Anecdotally, it is often reported to induce a state of relaxation and can act as a mild sedative. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is a key neurotransmitter responsible for reducing neuronal excitability. In other words, it can help calm.
Research suggests that damiana may interact with GABA receptors, contributing to its anxiolytic properties. Another study examining various damiana extracts further posits that its anxiolytic effects might be due to this interaction with GABA receptors.
How to Use Damiana
Damiana can be consumed in a variety of ways, each with its own unique benefits and considerations.
Tea
One of the most common methods of consumption is drinking tea. For how to prepare it, see below. This method allows for a soothing and relaxing experience, and the dosage can be easily adjusted according to your preferences.
Capsules and Tablets
Damiana is also available in capsule and tablet forms, which provide a convenient and straightforward method of consumption. These are typically standardized to contain a certain amount of active ingredients, ensuring a consistent dose. They can be taken with or without food.
Tinctures
Tinctures are another popular method of consumption. A tincture is a concentrated herbal extract that uses alcohol as a solvent and can be taken directly under the tongue or added to water or juice.
Smoking or Vaping
Damiana leaves can also be smoked or vaporized. This method allows for quick absorption of the active compounds into the bloodstream through the lungs, resulting in rapid onset of effects.
That said, you’ll have to consider the potential health implications of smoking anything, no matter what it is. Also, some of the base liquids used by certain vape juice manufacturers have been blamed for causing serious lung issues, so always pay attention to ingredients and the company’s reputation.
Remember, it’s crucial to start with a low dose and gradually increase it if necessary, paying attention to your body’s responses until you find the dosage that works best for you.
Preparation of Damiana Teas and Tinctures
While damiana can be consumed in various forms such as tea, capsules, tablets, tinctures, or smoking, the preparation process differs for each method.
Making Damiana Tea
Here’s how to make tea:
- Boil one cup of water in a pot
- Add a teaspoon of dried leaves to the boiling water
- Let the leaves steep in the water for about 15-20 minutes
- Strain the tea to remove the leaves, and your tea is ready to be consumed

Making Damiana Tinctures
To prepare a tincture:
- Fill a jar halfway with dried leaves.
- Pour vodka or another high-proof alcohol into the jar until the leaves are completely covered.
- Seal the jar and allow it to sit in a cool, dark place for at least 4 weeks.
- After this time, strain the mixture through a cheesecloth to separate the liquid from the leaves.
Dosage Information
The recommended dosage of damiana can vary depending on several factors, including the form of consumption, the desired effect, and individual sensitivity. It’s crucial to understand these guidelines to safely and effectively use this herb.
Suggested Amount by Method
- Tea: To make damiana tea, use approximately one teaspoon of dried damiana leaves per cup of hot water. This can be consumed 1-3 times daily.
- Capsules and Tablets: The typical recommended dosage in capsule or tablet form can vary, but generally, 400 – 800 mg per day is suggested. Check the manufacturer’s instructions for a more specific guideline.
- Tinctures: For tinctures, a common recommendation is to take 2-4 ml three times a day. As potency can vary, it’s advisable to follow the instructions on the bottle.
- Smoking or Vaping: For smoking or vaping, use a small pinch of dried leaves. It is important to note that this method should be used sparingly due to potential respiratory risks.
Please note that these are general suggestions and individual results may vary.
Known Side Effects of Damiana
While damiana is generally considered safe for most people, it’s still essential to address potential side effects. Like any substance, it might interact differently with each individual, leading to various responses that could be unpleasant.
More Common Side Effects
Though not felt by everyone, the most commonly reported side effects include:
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Some people may experience digestive discomfort, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea after consuming damiana, especially in high doses
- Insomnia: Despite its calming effects, excessive intake could potentially lead to insomnia or disturbed sleep patterns
- Hypoglycemia: Dangerously low blood sugar may be possible in individuals with diabetes or those on diabetes medication
- Allergic Reactions: In rare cases, an allergic reaction may occur, characterized by symptoms like itching, rash, swelling, severe dizziness, and trouble breathing
Remember, everyone reacts differently to herbal supplements, so you may want to start with small amounts first to assess your individual tolerance.

Risks and Warnings
While damiana is generally safe for most people when used in moderation, there are a few risks and warnings to consider:
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: It may stimulate menstrual flow, which could potentially cause a miscarriage. Therefore, it’s generally advised that pregnant and breastfeeding women avoid using it.
- Surgery: Because of its potential to affect blood sugar levels, it might interfere with blood sugar control during and after surgical procedures. It’s advisable to stop using it at least two weeks before a scheduled surgery.
- Blood Sugar Levels: Again, damiana might lower blood sugar levels, so If you have diabetes or are on diabetes medication, monitor your blood sugar closely and consult with your healthcare provider before using it
- Liver Disease: There are isolated reports of some users experiencing liver damage. If you have liver disease, use it with caution or avoid it altogether.
- Interaction with Other Drugs: Damiana might interact with various medications, including diabetes drugs, blood thinners, and lithium. Discuss this with your physician or otherwise research potential drug interactions before combining this with anything, no matter how insignificant it may seem.
Contraindications
Damiana may not be suitable for everyone. Certain situations or conditions might contraindicate its use:
- Existing Medical Conditions: People with certain health conditions such as liver disease, diabetes, or other chronic illnesses should consult with their healthcare provider before use. The herb may exacerbate these conditions or interfere with the effectiveness of prescribed medications.
- Use of Certain Medications: It may interact negatively with certain medications, leading to adverse effects. These medications can include blood thinners, diabetes treatment drugs, lithium, and others.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: As previously mentioned, its components may stimulate menstrual flow and potentially cause miscarriage. It is generally advised that pregnant and breastfeeding women avoid using it altogether.
- Allergies: Individuals allergic to plants in the Turneraceae family should obviously avoid damiana due to potential allergic reactions
- Low Iron in the Blood: Some of the components of damiana have been linked to iron deficiency in the past, so keep a close eye on things if this applies to you
Legal Status of Damiana
Damiana is legal in many countries, including the United States. There is an exception, however, within the United States. In the state of Louisiana, its sale is banned due to an extremely broad law prohibiting substances that have been used in some synthetic marijuana products.

Where to Buy Damiana
When searching for a reliable supplier, there are a few key factors to consider:
- Reputation: Look for suppliers with strong, positive reputations within the industry. You can often gauge this through customer reviews and testimonials. A supplier with a solid track record of quality and consistency is likely to be a safer choice.
- Quality Assurance: Ensure that the supplier provides quality assurance for their products. Suppliers should be able to provide certificates of analysis or lab reports that confirm potency, purity, and the absence of contaminants.
- Ethical Sourcing: Try to choose a supplier that practices ethical sourcing. This means that the product is harvested in a way that is sustainable and fair to the native communities where it’s grown.
- Transparent Communication: A reputable supplier should be able to answer your questions about their products clearly and honestly. Whether it’s about sourcing, processing, or storage of materials, they should be willing to share this information.
To find a supplier, search online for reputable botanical or herbal medicine retailers. You can also check out specialty shops in your area that carry botanical extracts if you are lucky enough to find one. Always take the time to do your research and don’t be afraid to ask questions to ensure you’re getting a high-quality product.
Conclusion
In conclusion, damiana is an alternative herbal supplement that offers several health benefits, from boosting mental well-being to enhancing sexual health. However, some individuals may notice some side effects, which are mostly mild but can vary with individual body chemistry
If you have a medical doctor that you usually visit or speak with, discuss damiana with them before use because it may interact with some medications or be a bad idea if you have certain preexisting conditions.
Finally, when you’re sourcing it, look for a vendor who has a reputation for providing high-quality products and is eagerly responsive in its customer support responsibilities.


Latest from our blog
Please Read….This is Urgent
In loving memory of Ryan, a special individual who recently passed away, we honor his [...]
Damiana Exposed: Special Look At Turnera diffusa (2023)
Damiana Exposed: Special Look At Turnera diffusa (2023) Damiana is a wild shrub native to [...]
Kanna: A New Look At An Exciting Mood Booster (2023)
What is kanna? Some say the botanical has similar effects to MDMA, or ecstasy. Others [...]
Blue Lotus Flower: Unveiling Its Mystical & Therapeutic Powers
To cut to the chase and pickup potent 25x blue lotus extract today while enjoying [...]
Red Bubble Kratom Extraction: A Comprehensive Guide
As a kratom enthusiast, have you ever wondered if there was a method for getting [...]
Aug
Maeng Da Kratom 101: Accurate Info You Can Trust
Maeng Da kratom may be the most popular kratom strain on the market today. The [...]
Aug